Treatment tag: clear, practical help for real medication questions
Need straightforward advice about treatments? This tag collects easy-to-read guides on common drugs, alternatives, side effects, and safe ways to buy medicine. We focus on real problems—what a medicine does, who should avoid it, how it compares to other options, and smart safety checks before you try it.
What you’ll find here
Scan this tag when you need a quick, reliable answer. You'll find drug deep dives (like Reminyl for dementia and Zithromax for infections), comparisons (Formoterol/budesonide vs other inhalers), safety explainers (Ativan and heart risks, hyponatremia in the elderly), and practical buying tips (how to buy Topamax, Isordil, or methyldopa online safely). There are also pieces on alternatives—antidepressants, antipsychotics, GI drugs—and reviews of online pharmacies to help you spot legit sellers.
Each article gives: what the drug treats, how it works in plain language, common side effects, who should avoid it, and simple steps to stay safe. We don’t hide the tradeoffs. If a medicine raises weight or heart risk, you’ll read that up front. If an online pharmacy is questionable, we tell you what to watch for.
Quick ways to use these guides
1) Search by symptom or drug name. Want alternatives to Duloxetine or Hydroxychloroquine? You'll see options and what changes to expect. 2) Check safety sections first—especially interactions and age-specific warnings. 3) If you’re ordering medicine online, read our pharmacy reviews and the customs/import guide for the USA before you click buy.
Before you act on anything here, pause and ask: Do I need a prescription? Do I have conditions (heart, pregnancy, kidney) that change risk? Could this interact with my current meds? If the answer is unclear, call your prescriber or pharmacist. Our goal is to inform, not replace direct medical advice.
Short, useful examples: if you wonder about a benzodiazepine and heart risk, our Ativan piece summarizes cardiology facts and practical safety tips. If weight gain is a worry, check the Abilify alternatives article for newer drugs with lower metabolic risk. For breathing meds, the inhaler comparison helps you pick what works fastest and fits your insurance.
We also help with non-prescription choices—supplements like Lasuna or raspberry ketone are explained with benefits and side effects so you can decide sensibly. And if you're caring for an older adult, read the hyponatremia and promethazine (Phenergan) guides to avoid common pitfalls.
Use this tag as a starting point. Read one article, then check a second for alternative views. When in doubt, talk to a clinician. If you want a personalized recommendation on which posts to read first, tell me your condition or medicine and I’ll point you to the most relevant articles.
26
Labetalol for Anxiety: Can It Help?
In my latest blog post, I explored the potential benefits of using labetalol for anxiety. Labetalol is a medication typically prescribed for treating high blood pressure, but it has also shown some promise in helping those suffering from anxiety. From my research, it appears that labetalol can help by blocking the effects of stress hormones, thus reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety. However, it's important to note that this medication may not be suitable for everyone and should only be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Overall, labetalol might be a helpful option for some individuals struggling with anxiety, but more research is needed to fully understand its potential benefits.
6
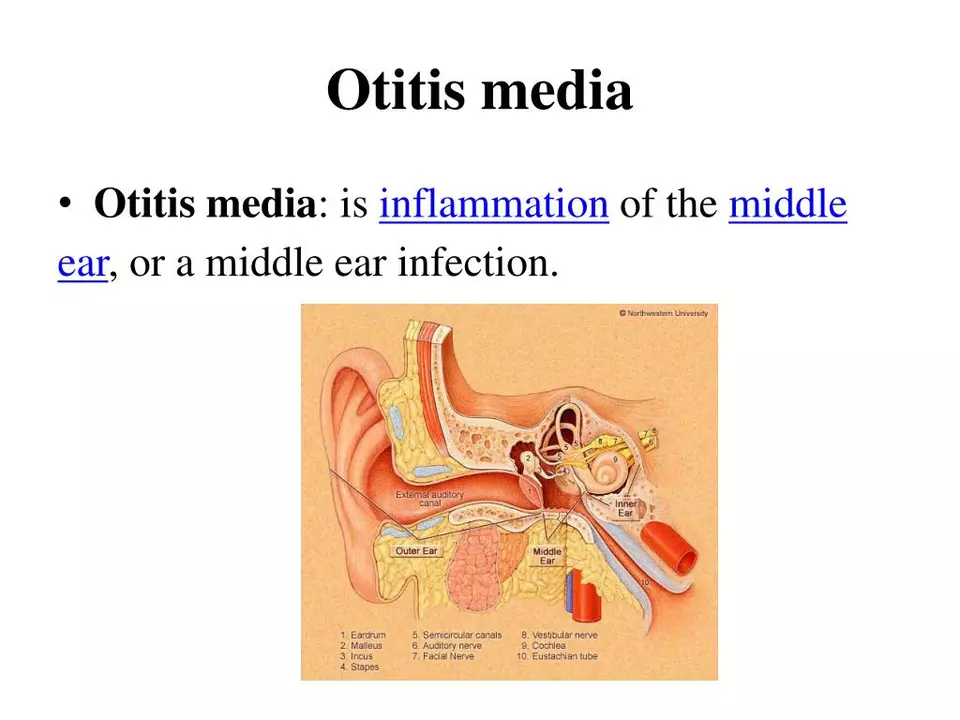
The connection between azelastine and otitis media
As a blogger, I've been researching the connection between azelastine and otitis media, and I've discovered some interesting findings. Azelastine, a popular antihistamine, has been shown to potentially help in treating otitis media, a common middle ear infection. By reducing inflammation and congestion, azelastine helps to alleviate some of the symptoms associated with this condition. However, it's important to note that azelastine is not a standalone treatment for otitis media, and should be used in conjunction with other medications prescribed by a healthcare professional. Overall, azelastine seems to be a promising adjunct therapy for otitis media, but further research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness.