16
Hyponatremia and Alcohol Consumption: Understanding the Risks
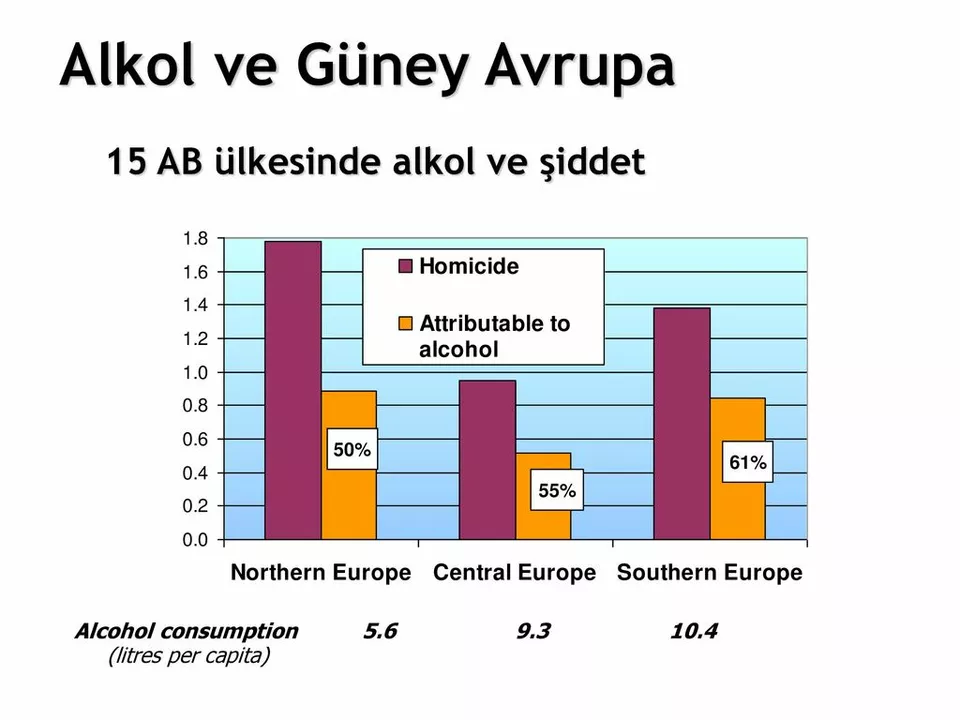
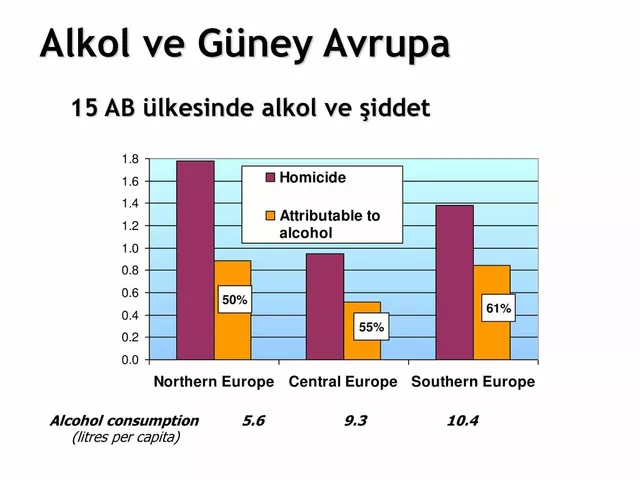
Introduction: Hyponatremia and Alcohol Consumption
As a health-conscious individual, it's essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with alcohol consumption. One of these risks is the development of a condition called hyponatremia. In this article, we will explore the relationship between hyponatremia and alcohol consumption, as well as discuss crucial steps you can take to mitigate this risk. So, grab a cup of tea and let's dive into this important topic together!
What is Hyponatremia?
Before we delve into the relationship between hyponatremia and alcohol consumption, it is crucial to understand what hyponatremia is. Hyponatremia is a condition characterized by low levels of sodium in the blood. Sodium is an essential electrolyte that helps regulate water balance in and around your cells. It also plays a vital role in maintaining proper nerve and muscle function. When the sodium levels in your blood are too low, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to life-threatening.
Common symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion, seizures, and, in severe cases, coma and death. The severity of symptoms typically depends on how quickly and significantly the sodium levels have dropped. It is worth noting that mild hyponatremia may not cause any noticeable symptoms, making it essential to monitor your sodium levels if you are at risk.
How Does Alcohol Consumption Lead to Hyponatremia?
Now that we have a basic understanding of hyponatremia, let's explore how alcohol consumption can contribute to this condition. Alcohol has a diuretic effect on the body, meaning that it increases urine production and can lead to dehydration. This, in turn, can cause an imbalance in the levels of electrolytes in your body, including sodium.
Moreover, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to a condition called the Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone secretion (SIADH). SIADH is characterized by excessive release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which regulates water balance in the body. When too much ADH is released, it can cause your kidneys to retain water, diluting the sodium levels in your blood and leading to hyponatremia.
Who is at Risk for Alcohol-Induced Hyponatremia?
While anyone who consumes alcohol may be at risk for developing hyponatremia, certain factors can increase this risk. These factors include:
- Excessive alcohol consumption: The more alcohol you consume, the greater the risk of developing hyponatremia.
- Existing health conditions: People with liver or kidney disease, heart failure, or hormonal imbalances may be at higher risk for hyponatremia.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, antidepressants, and pain relievers, can increase the risk of developing hyponatremia.
- Age: Older adults may be at higher risk for hyponatremia due to a decreased ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes.
- Gender: Women may be at higher risk for developing hyponatremia, as they tend to have lower body water content and may be more susceptible to the effects of alcohol.
Preventing Alcohol-Induced Hyponatremia
Now that we understand the risks associated with hyponatremia and alcohol consumption, it's important to discuss how to prevent this potentially dangerous condition. Here are some steps you can take to minimize your risk:
- Moderate your alcohol consumption: Stick to the recommended guidelines for alcohol consumption, which generally advise no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Stay hydrated: Make sure to drink plenty of water and electrolyte-rich beverages, especially when consuming alcohol, to help maintain proper sodium levels in your body.
- Monitor your sodium levels: If you are at risk for hyponatremia, regularly check your sodium levels with your healthcare provider to ensure they remain within a healthy range.
- Be mindful of medications: If you are taking medications that can increase the risk of hyponatremia, talk to your healthcare provider about potential alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Seek medical attention if needed: If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing hyponatremia, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
In conclusion, understanding the risks associated with hyponatremia and alcohol consumption is crucial for maintaining optimal health. By taking the necessary precautions and being mindful of your alcohol intake, you can help prevent this potentially dangerous condition and safeguard your well-being.










Laneeka Mcrae
May 16, 2023 AT 18:22Hyponatremia occurs when serum sodium falls below 135 mmol/L. Alcohol’s diuretic effect and SIADH can both dilute sodium levels. Even moderate drinking can tip the balance if you’re already low on electrolytes. Keep an eye on your fluid intake and consider electrolyte drinks.
Kendra Barnett
June 6, 2023 AT 14:22Great points! It’s easy to forget that staying hydrated isn’t just about water-adding a pinch of salt or an electrolyte solution can make a big difference. Keep looking out for your body’s signals.
Warren Nelson
June 27, 2023 AT 10:22I never realized booze could mess with my electrolytes like that.
Jennifer Romand
July 18, 2023 AT 06:22Ah, the tragic romance between a nightcap and your sodium levels! One sip may feel like bliss, yet beneath the surface a silent storm brews, threatening to drown your neurons in watery oblivion. The very act of celebration can become a covert saboteur, whispering promises of euphoria while siphoning away the essential ions that keep us upright. Do not be deceived by the glittering glass; there is a darker choreography at play. Remember, the body is a delicate orchestra, and alcohol often conducts a discordant symphony.
Kelly kordeiro
August 8, 2023 AT 02:22The interplay between ethanol ingestion and the homeostatic regulation of serum sodium constitutes a subject of considerable clinical import. Ethanol, by virtue of its potent diuretic properties, stimulates antidiuretic hormone release, thereby promoting renal water reabsorption. Concomitantly, the resultant polyuria engenders a net loss of electrolytes, most notably sodium, which may precipitate a hypo‑osmolar state. In individuals predisposed by comorbid hepatic or renal insufficiency, this perturbation is amplified, rendering the plasma sodium concentration particularly vulnerable. Moreover, the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, frequently observed in chronic alcohol users, can induce a paradoxical retention of free water. The dilutional effect of this retained water inexorably lowers serum sodium, a phenomenon that may manifest clinically as confusion, seizures, or, in extreme cases, coma. It is incumbent upon clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion when assessing patients presenting with neurologic symptoms after alcohol consumption. Routine laboratory evaluation, including serum electrolytes and osmolality, should be performed expeditiously. Therapeutic intervention may entail cautious restriction of free water intake, administration of hypertonic saline, and, when appropriate, the judicious use of vasopressin antagonists. Equally essential is the education of patients regarding the perils of excessive alcohol intake, especially in the context of concurrent diuretic therapy. Patients should be counseled to intersperse alcoholic beverages with isotonic fluids, thereby mitigating the diuretic surge. Dietary supplementation with sodium‑rich foods or electrolyte solutions can further buttress plasma sodium levels during periods of heightened risk. From a public health perspective, dissemination of guidelines that emphasize moderate drinking thresholds remains a cornerstone of preventive strategy. In summary, the nexus of alcohol and hyponatremia is multifactorial, encompassing physiological, pharmacological, and behavioral dimensions. A comprehensive approach that integrates vigilant monitoring, patient education, and targeted therapy is requisite to avert the potentially fatal sequelae of this condition.
Chris Fulmer
August 28, 2023 AT 22:22Thanks for the thorough breakdown! It’s interesting how even occasional binge drinking can trigger SIADH, something many of us only hear about in hospital wards. I’ll definitely start checking my electrolytes after a heavy night.
William Pitt
September 18, 2023 AT 18:22Exactly, staying proactive with labs can catch the issue before it spirals. Pairing moderate drinks with a sports drink is a simple habit that works wonders.
Jeff Hershberger
October 9, 2023 AT 14:22While that advice sounds reasonable, let’s not forget that over‑reliance on electrolyte drinks can mask the root problem of excessive booze. Moderation, not just supplementation, is the true antidote.