18
Pepcid (Famotidine) vs Alternatives: Detailed Comparison of Acid‑Reflux Meds

Acid Reflux Medication Selector
Find Your Best Acid Reflux Medication
Answer a few questions to get personalized recommendations for your heartburn treatment.
Your Recommendation
When it comes to treating heartburn, Pepcid (generic name famotidine) is a widely used histamine‑2 (H2) blocker that reduces stomach acid production. But Pepcid isn’t the only option on the market. Many people wonder whether another H2 blocker, a proton‑pump inhibitor (PPI), or even a simple antacid might work better for their symptoms, cost profile, or lifestyle. This guide breaks down the most common alternatives, compares them across key criteria, and helps you decide which drug fits your needs.
Why Compare? The Jobs You’re Trying to Solve
- Identify the core differences between famotidine and its closest competitors.
- Understand how H2 blockers stack up against PPIs for short‑term and long‑term relief.
- Figure out side‑effect profiles and drug‑interaction risks.
- Match price and accessibility to your budget and insurance coverage.
- Know when a non‑prescription option like an antacid might be enough.
How the Comparison Works
We’ll evaluate each medication on five practical dimensions:
- Mechanism of action - How the drug reduces acid.
- Onset & duration - How quickly it works and how long relief lasts.
- Effectiveness for different conditions - Heartburn, GERD, ulcers, etc.
- Safety & side‑effects - Common complaints and serious warnings.
- Cost & availability - Prescription vs OTC, Australian pricing, and insurance coverage.
Core Players in the Acid‑Reflux Market
The most relevant alternatives fall into three categories:
- Other H2 blockers - cimetidine, ranitidine (withdrawn in many countries), and nizatidine.
- Proton‑pump inhibitors - omeprazole, lansoprazole, and esomeprazole.
- Over‑the‑counter antacids - calcium carbonate, magnesium‑aluminium hydroxide blends.
Quick Reference Table
| Medication | Drug class | Typical dose (adult) | Onset | Duration of relief | Effectiveness (mild‑moderate heartburn) | Common side‑effects | Australian OTC status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepcid | H2 blocker | 20 mg once or twice daily | 30‑60 min | 8‑12 h | Good | Headache, dizziness, constipation | Prescription (low‑dose 10 mg OTC) |
| Cimetidine | H2 blocker | 200 mg twice daily | 45‑90 min | 8‑12 h | Moderate | Gynecomastia, liver enzyme rise | Prescription |
| Ranitidine | H2 blocker | 150 mg twice daily | 30‑60 min | 8‑12 h | Good (where available) | Rare NDMA impurity concerns | Mostly withdrawn |
| Omeprazole | PPI | 20 mg once daily | 1‑4 h | 24 h+ | Excellent for severe GERD | Headache, diarrhea, long‑term B12 deficiency | OTC (20 mg) |
| Lansoprazole | PPI | 15 mg once daily | 1‑4 h | 24 h+ | Very effective for ulcers | Similar to omeprazole, higher cost | Prescription |
| Esomeprazole | PPI | 20 mg once daily | 1‑4 h | 24 h+ | Top tier for Barrett’s esophagus | Headache, nausea, higher price | Prescription |
| Calcium carbonate antacid | Antacid | 500‑1000 mg as needed | 5‑10 min | 1‑2 h | Brief relief for occasional heartburn | Gas, constipation | OTC |
Deep Dive: H2 Blockers vs PPIs
Both drug families lower stomach acid, but they do it in different places. H2 blockers like Pepcid comparison block histamine receptors on parietal cells, stopping a signal that tells the cells to pump acid. PPIs, on the other hand, irreversibly inhibit the proton pump itself - the final step in acid production. This difference explains why PPIs tend to have a longer lasting effect but also a higher risk of nutrient malabsorption when used for months.
For people with occasional heartburn, an H2 blocker’s quicker onset and lower cost make it a sensible first line. However, if you have erosive esophagitis, a PPI’s stronger and more sustained suppression is usually recommended by gastroenterologists.
Safety and Interaction Highlights
Every medication carries a safety checklist. Below are the most relevant points for each class.
- Pepcid (famotidine) - Generally safe in pregnancy (Category B2 in Australia). Rarely interacts with warfarin; monitor INR if you’re on blood thinners.
- Cimetidine - Strong CYP450 inhibitor; can raise levels of drugs like theophylline, carbamazepine, and certain antihistamines.
- Ranitidine - Historically safe, but NDMA contamination led to worldwide recalls in 2024. Use only if a verified, impurity‑free supply is confirmed.
- Omeprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole - Long‑term use (>8 weeks) linked to low magnesium, B12 deficiency, and increased risk of Clostridioides difficile infection. Discuss tapering plans with your doctor.
- Antacids - Can interfere with absorption of antibiotics like tetracycline and fluoroquinolones if taken simultaneously.
Cost and Accessibility in Australia (2025)
Price data comes from the Australian Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) and major pharmacy chains as of October 2025.
- Pepcid (famotidine) - 20 mg 28‑tablet pack: AUD 12.90 (PBS‑listed) for prescription; low‑dose 10 mg OTC pack: AUD 9.50.
- Cimetidine - Prescription only; 200 mg 28‑tablet pack: AUD 14.30.
- Omeprazole - 20 mg OTC pack (28 tablets): AUD 19.80; PBS‑subsidised prescription: AUD 7.70.
- Lansoprazole - Prescription; 15 mg pack: AUD 22.00.
- Esomeprazole - Prescription premium; 20 mg pack: AUD 30.00.
- Calcium carbonate (Tummys) - 500 mg chewable tablets, 100‑tablet bottle: AUD 6.40.
Most PBS‑listed medicines require a doctor’s script, but the out‑of‑pocket cost is still lower than many private‑label brand PPIs. If you have private health insurance, check whether the pharmacy benefits cover the brand you prefer.
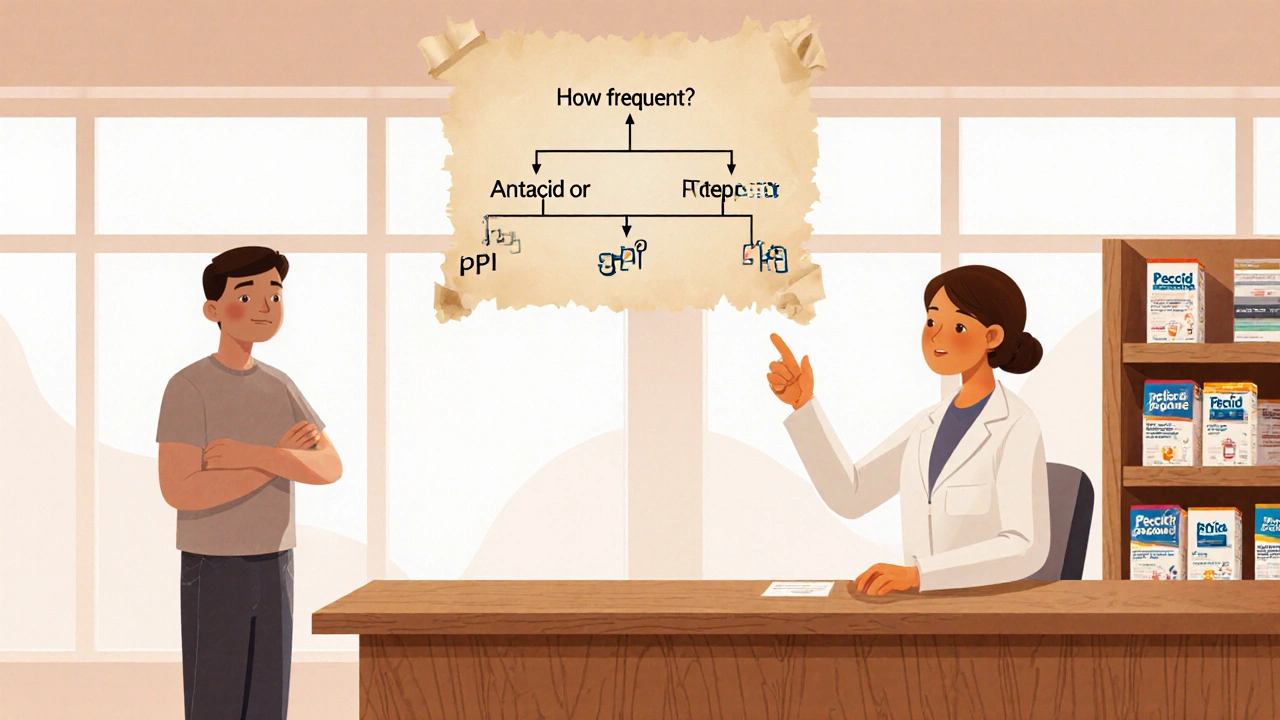
Choosing the Right Option for Your Situation
Here’s a quick decision tree you can run through before you head to the pharmacy:
- How frequent is your heartburn?
• Occasional (1‑2 times/month) → Try an antacid or 10 mg famotidine OTC.
• Frequent (weekly) → Move to full‑dose Pepcid or another H2 blocker. - Any diagnosed condition (GERD, ulcer, Barrett’s)?
• Yes → A PPI (omeprazole first‑line) is usually recommended.
• No → H2 blocker remains a safe, inexpensive choice. - Do you take other prescription meds?
• On blood thinners, anti‑epileptics, or theophylline? → Avoid cimetidine; famotidine is safer. - Concern about long‑term side‑effects?
• Want to limit nutrient deficiencies? → Stick with H2 blocker for < 8 weeks, then reassess.
Always discuss chronic symptoms with a GP. They can order an endoscopy if you have alarm signs such as difficulty swallowing, weight loss, or vomiting blood.
Practical Tips for Using Pepcid and Its Peers
- Take H2 blockers 30 minutes before meals for best results.
- PPIs work best when taken 30 minutes before breakfast; don’t split the dose.
- Never crush or chew extended‑release tablets; it destroys the coating.
- If you need to combine an antacid with a PPI/H2 blocker, space them at least two hours apart.
- Store all medicines in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Bottom Line
For most Australians dealing with mild‑to‑moderate heartburn, famotidine (Pepcid) offers a balanced mix of speed, duration, safety, and price. When symptoms are more severe or persistent, stepping up to a PPI such as omeprazole is usually justified, provided you monitor for long‑term side‑effects. Alternatives like cimetidine still have a role for patients who can’t take famotidine, but be mindful of drug interactions. And never dismiss the power of simple antacids for occasional flare‑ups - they’re cheap, fast, and OTC.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take Pepcid and a PPI at the same time?
Generally it’s not needed because both lower acid. If a doctor prescribes both, they’ll usually space them two hours apart to avoid reduced absorption of the PPI.
Is famotidine safe during pregnancy?
Famotidine is classified as Category B2 in Australia, meaning animal studies show no risk but there are no well‑controlled human studies. Many doctors consider it acceptable when the benefit outweighs potential risk.
Why was ranitidine removed from the market?
In 2024 regulators found that ranitidine could contain the probable carcinogen NDMA above safe limits. Most manufacturers halted production worldwide, although some impurity‑free batches re‑appeared under strict controls.
How long can I safely use a PPI?
Short‑term (4‑8 weeks) treatment is standard for most reflux cases. For chronic conditions, a doctor may keep you on a low dose for years but will periodically check magnesium, B12, and bone density.
Do antacids interfere with other medicines?
Yes. Antacids can bind to antibiotics like tetracycline or fluoroquinolones, reducing their absorption. Take antacids at least two hours apart from those drugs.




Rajesh Singh
October 18, 2025 AT 13:13Honestly, the way people gulp down PPIs like candy is a slap in the face to common sense.
These drugs are meant for short bursts, not a lifetime Netflix binge of acid suppression.
If you skip the warning labels, you’re basically signing a pact with a silent thief that steals your magnesium, B12 and even your gut’s natural rhythm.
Famotidine, for example, offers a middle ground-fast enough to rescue a flare‑up, subtle enough not to hijack your microbiome.
Choosing the cheap, over‑the‑counter antacid when the heartburn is occasional is a virtue worth practicing.
Remember, a mindful diet and timing your meals can often out‑perform a daily chemical blanket.
Albert Fernàndez Chacón
October 26, 2025 AT 02:33Looks like the guide covers all the bases-mechanism, onset, cost, and safety.
The table makes it easy to compare famotidine with the PPIs at a glance.
If you only get heartburn once a month, the cheap calcium carbonate is probably enough.
For chronic GERD, a low‑dose PPI under doctor supervision stays the gold standard.
Drew Waggoner
November 2, 2025 AT 14:53Skipping famotidine for a PPI without a doctor’s note feels like playing roulette with your gut lining.
Mike Hamilton
November 10, 2025 AT 04:13i think it’s important to look at the cultural context of med choices.
in australia the PBS subsidies shape what people actually pick.
the guide mentions that famotidine OTC is pricier than a generic PPI prescription, which can be surprising for newcomers.
people also forget that cimetidine’s interaction profile can mess with other meds you’re already on.
overall, the balance between cost and safety is a personal calculus.
Liberty Moneybomb
November 17, 2025 AT 17:33What the pharmaceutical lobby doesn’t tell you is that every new “advanced” acid‑blocker comes with a hidden agenda to lock you into a decade‑long subscription.
They whisper that PPIs are safer, then quietly fund the studies that hide the magnesium‑draining side effects.
Meanwhile, the cheap famotidine sits on the shelves like a rebel, waiting for the brave enough to pick it up without a shiny billboard.
Some say the FDA fast‑tracked omeprazole because of back‑room deals, and the NDMA scare with ranitidine felt more like a staged drama than a true safety issue.
If you’re reading this, you’re already skeptical, and that’s a good thing-question the “standard of care” and you’ll see the profit motives glittering behind every guideline.
The real truth is that most people could manage with diet tweaks and an antacid, but the machine pushes you toward the pricey, long‑term fix.
Don’t let the glittering promises of “quick relief” blind you to the slow erosion of your body’s natural balance.
Alex Lineses
November 25, 2025 AT 06:53Great point on the cost‑benefit analysis. When you factor in the pharmacoeconomic data, famotidine’s ICER (incremental cost‑effectiveness ratio) remains favorable compared to generic PPIs for intermittent symptoms. Moreover, the drug‑drug interaction profile is clean, which is a huge plus for polypharmacy patients. Keep an eye on the upcoming biosimilar H2 blockers-they might shift the market dynamics even further.
Brian Van Horne
December 2, 2025 AT 20:13Thus, the fiscal prudence aligns with clinical prudence-an elegant equilibrium.
Margaret pope
December 10, 2025 AT 09:33i love how you pointed out the australian subsidy angle its really helpful for people trying to make sense of pricing and safety it shows that you cant ignore local policies
Karla Johnson
December 17, 2025 AT 22:53When evaluating acid‑reflux therapies, it is essential to adopt a systematic, evidence‑based mindset rather than relying on anecdotal preferences.
The pharmacodynamics of H2 blockers versus proton‑pump inhibitors dictate distinct clinical outcomes, and conflating the two can lead to suboptimal management.
Famotidine, for instance, achieves peak plasma concentration within an hour, providing rapid symptom relief that is particularly useful for breakthrough heartburn episodes.
Conversely, PPIs such as omeprazole require activation in the acidic canaliculi of parietal cells, resulting in a delayed onset but prolonged suppression of gastric acid secretion.
This kinetic disparity explains why many gastroenterologists reserve PPIs for erosive esophagitis and ulcer disease while recommending H2 blockers for sporadic dyspepsia.
Cost considerations further reinforce this hierarchy; the PBS data illustrate that a 20 mg famotidine pack costs roughly AUD 12.90, whereas a comparable 20 mg omeprazole pack incurs a higher out‑of‑pocket expense when not subsidised.
Insurance coverage nuances also matter, as private health plans may cap reimbursable amounts for brand‑name PPIs, nudging patients toward generic alternatives.
Safety profiles cannot be ignored: long‑term PPI use has been linked to hypomagnesemia, vitamin B12 deficiency, and an elevated risk of Clostridioides difficile infection, all of which demand periodic laboratory monitoring.
In contrast, famotidine’s adverse event spectrum is relatively benign, typically limited to mild headache or constipation, and it does not significantly interfere with cytochrome P450 metabolism.
This pharmacokinetic advantage is particularly relevant for patients on anticoagulants, antiepileptics, or theophylline, where drug‑drug interactions could be catastrophic.
Nevertheless, clinicians must remain vigilant about the potential for tachyphylaxis with H2 blockers, a phenomenon where tolerance develops after several weeks of continuous use.
If tolerance emerges, a brief drug holiday or rotation to a different class can restore therapeutic efficacy.
Practical administration tips-such as taking H2 blockers 30 minutes before meals and PPIs before breakfast-optimize drug absorption and maximize patient outcomes.
Finally, shared decision‑making empowers patients to weigh the trade‑offs between rapid relief, long‑term safety, and financial burden, leading to personalized treatment plans that align with individual health goals.
Linda A
December 25, 2025 AT 12:13One could argue that the true balance lies not in the pill but in the mindful awareness of hunger and stress.