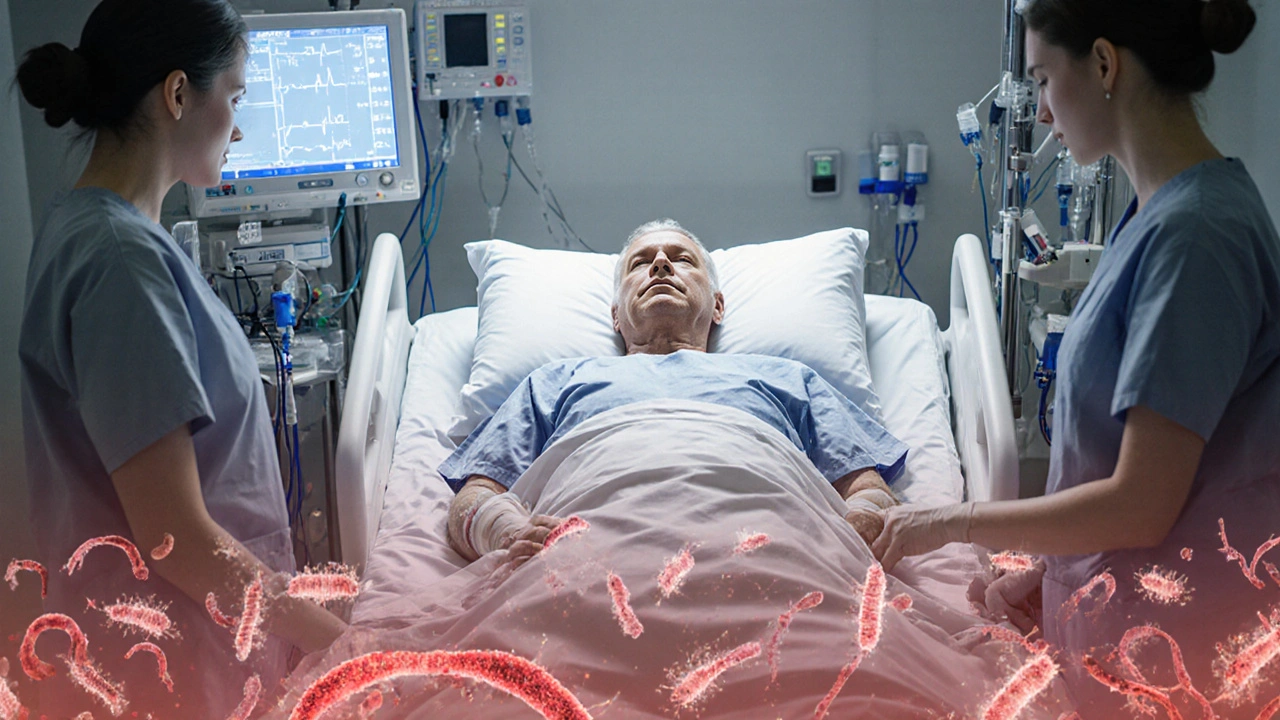
Antifungal Resistance: Why It Matters and How to Fight It
When dealing with antifungal resistance, the ability of fungi to survive drugs that would normally kill or stop them. Also called fungal drug resistance, it threatens modern medicine. Candida species, common yeasts that cause infections from thrush to bloodstream sepsis are the most frequent culprits, especially when they acquire azole resistance, a loss of sensitivity to the main class of oral antifungal agents. Tackling the problem starts with antifungal stewardship, coordinated actions to use antifungals wisely and curb resistance. The rise of resistant strains shows why understanding antifungal resistance is essential for patients and clinicians alike.
What Drives Fungal Drug Resistance?
At the core, antifungal resistance hinges on three drug‑resistance mechanisms: genetic mutations that alter drug targets, over‑expression of efflux pumps that push medication out of the cell, and biofilm formation that creates a protective barrier. For example, a point mutation in the ERG11 gene of Candida can reduce azole binding, while up‑regulated CDR1 pumps expel the drug before it reaches its target. Biofilms on catheters act like a shield, making even high‑dose therapy ineffective. Understanding these mechanisms lets clinicians predict which drugs will work and where they might fail.
These mechanisms don’t act in isolation. A strain with an ERG11 mutation often also boosts its efflux pump activity, creating a multi‑layered defense. This compounding effect means that a single laboratory test may miss the full picture, prompting the need for comprehensive susceptibility panels. When labs report a “susceptible‑dose dependent” result, it’s a cue that higher doses or combination therapy might be required.
Patients with compromised immune systems—such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation—are especially vulnerable. Their bodies provide a fertile ground for resistant fungi to flourish, and the limited drug options heighten the stakes. In these cases, clinicians must balance the risk of toxicity with the need for aggressive antifungal regimens.
Diagnosing resistance early can change outcomes. Rapid molecular tests that detect ERG11 mutations or CDR1 over‑expression are becoming more common in tertiary hospitals. When a test flags a resistant genotype, physicians can pivot to alternative classes like echinocandins or the newer tetrazoles, avoiding a fruitless course of azoles.
Therapeutic choices are guided by both the organism and the resistance profile. Echinocandins target the fungal cell wall and remain effective against many azole‑resistant strains, but they’re expensive and administered intravenously. New oral agents such as ibrexafungerp offer a bridge, delivering echinocandin‑like activity in a pill. However, resistance to these newer drugs is already emerging, underscoring the need for vigilant stewardship.
Antifungal stewardship programs bring together pharmacists, infectious‑disease physicians, and microbiology labs to monitor usage patterns, enforce formulary restrictions, and educate staff. Core actions include reviewing every antifungal prescription within 48 hours, de‑escalating therapy based on culture results, and limiting prophylactic azole use in high‑risk units. Data from stewardship dashboards often reveal over‑prescription trends that can be corrected before resistance spreads.
Research is racing to outpace resistance. Scientists are exploring combination therapies—pairing azoles with statins or with immune‑modulating agents—to overcome efflux pump defenses. Meanwhile, genomics‑driven drug discovery is identifying novel targets beyond the traditional ergosterol pathway. As these innovations move from bench to bedside, clinicians will gain more weapons against stubborn fungal infections.
All these topics converge in the collection below. Whether you’re looking for practical tips on buying cheap generic drugs, deep dives into specific antifungal comparisons, or updates on emerging infectious threats, the articles ahead cover the breadth of antifungal resistance and its real‑world impact. Dive in to find the exact guidance you need.
9
Candidemia and Disseminated Candida Infections: How They Strain the Healthcare System
Explore how candidemia and disseminated Candida infections affect hospital costs, patient outcomes, and healthcare resources, and learn strategies to reduce their impact.
Latest Posts
Popular Posts
-
 OTC Heartburn Medications: Antacids, H2 Blockers & PPIs Explained
OTC Heartburn Medications: Antacids, H2 Blockers & PPIs Explained
-
 Meniere’s Diet: How Sodium Restriction and Fluid Balance Reduce Vertigo and Hearing Loss
Meniere’s Diet: How Sodium Restriction and Fluid Balance Reduce Vertigo and Hearing Loss
-
 Enteral Feeding Tube Medication Safety: Compatibility and Flushing Protocols Explained
Enteral Feeding Tube Medication Safety: Compatibility and Flushing Protocols Explained
-
 Accidental Pediatric Medication Overdose: How to Prevent It and What to Do If It Happens
Accidental Pediatric Medication Overdose: How to Prevent It and What to Do If It Happens
-
 Duloxetine and Liver Health: What You Need to Know About Hepatotoxicity Risk
Duloxetine and Liver Health: What You Need to Know About Hepatotoxicity Risk



